Your skin helps protect you from germs,
but sometimes it can get infected by them.
Some common types of skin infections are:
- Bacterial: Cellulitis, impetigo and Staphylococcal infections
- Viral: Shingles, warts, and herpes simplex
- Fungal: Athlete’s foot and yeast infections
- Parasitic: Body lice, head lice, and scabies
Bacterial Skin Infections
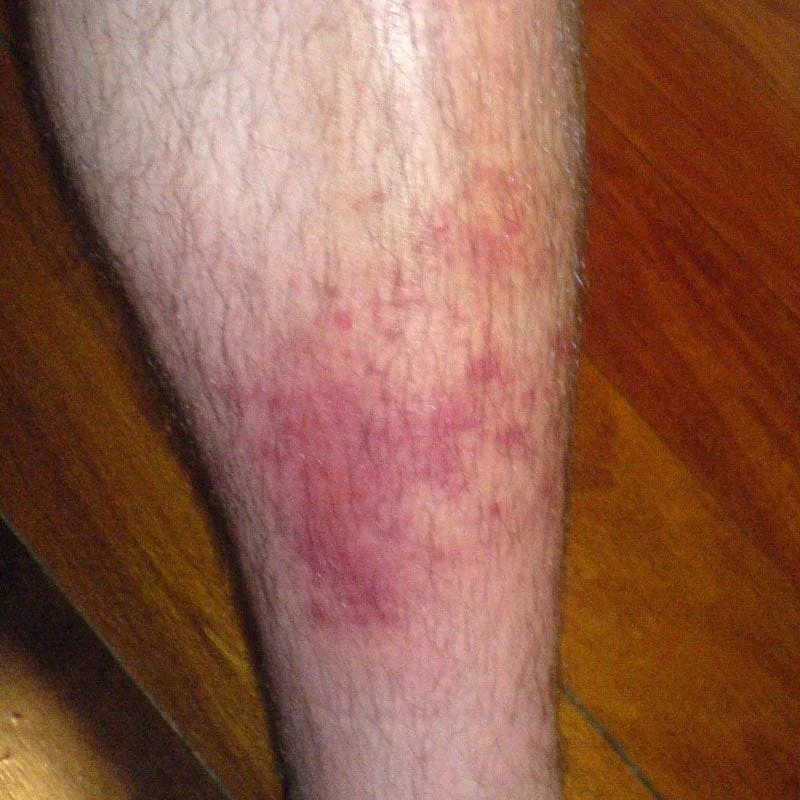
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin and deep underlying tissues. Group A strep (streptococcal) bacteria are the most common cause. The bacteria enter your body when you get an injury such as a bruise, burn, surgical cut, or wound.
Symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Swollen glands or lymph nodes
- A rash with painful, red, tender skin
- The skin may blister and scab over
Your health care provider may take a sample or culture from your skin or do a blood test to identify the bacteria causing infection. Treatment is with antibiotics. They may be oral in mild cases, or intravenous (through the vein) for more severe cases.
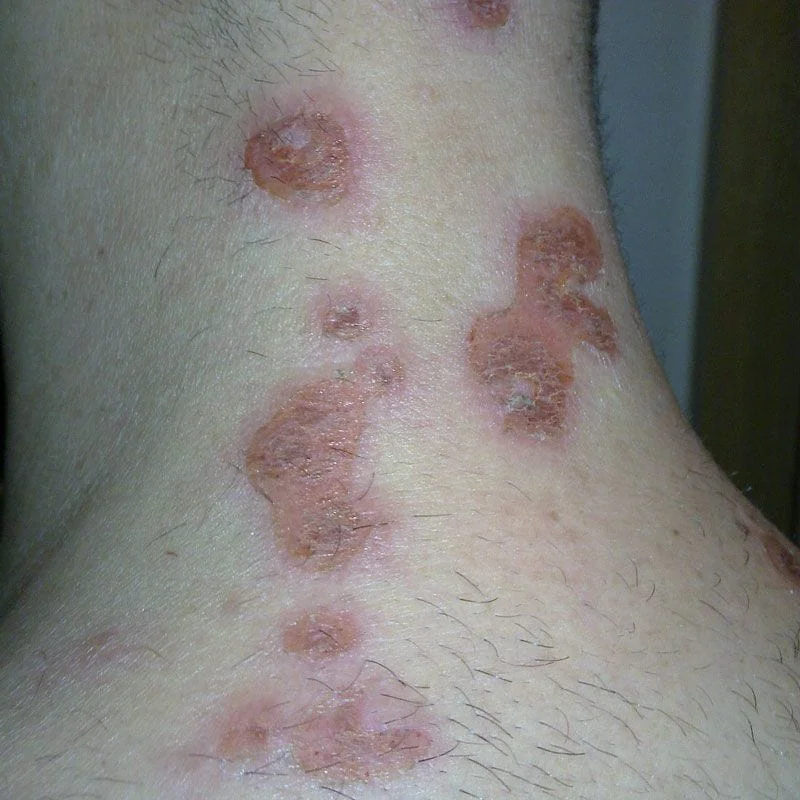
Impetigo
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by bacteria. It is usually caused by staphylococcal (staph) bacteria, but it can also be caused by streptococcal (strep) bacteria. It is most common in children between the ages of two and six. It usually starts when bacteria get into a break in the skin, such as a cut, scratch, or insect bite.
Symptoms start with red or pimple-like sores surrounded by red skin. These sores can be anywhere, but usually they occur on your face, arms and legs. The sores fill with pus, then break open after a few days and form a thick crust. They are often itchy, but scratching them can spread the sores.
Impetigo can spread by contact with sores or nasal discharge from an infected person. You can treat impetigo with antibiotics.
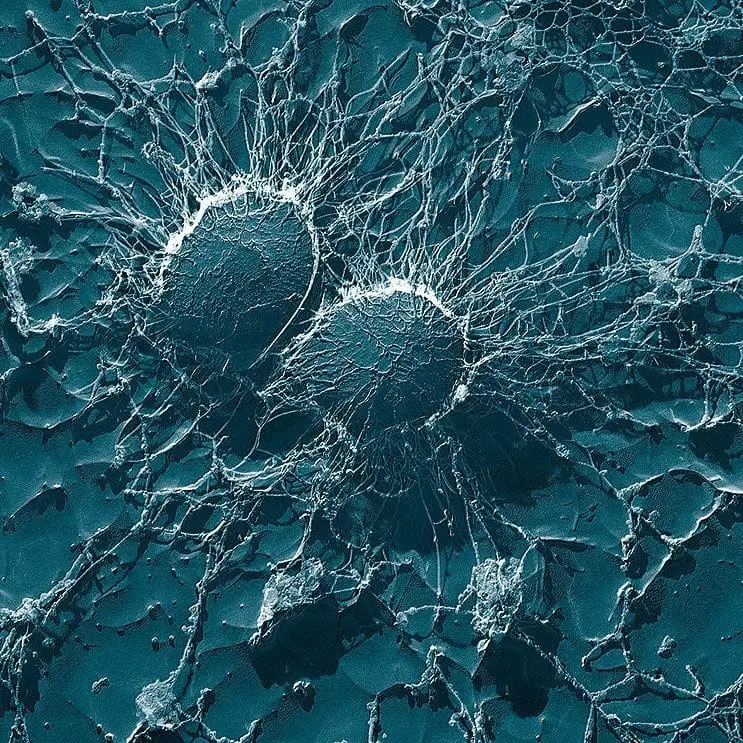
Staph is short for Staphylococcus, a type of bacteria. Skin infections caused by variant Staphylococcus aureus can look like pimples or boils. They may be red, swollen and painful, and sometimes have pus or other drainage. They can turn into impetigo, which turns into a crust on the skin, or cellulitis, a swollen, red area of skin that feels hot.
Anyone can get a staph skin infection. You are more likely to get one if you have a cut or scratch, or have contact with a person or surface that has staph bacteria. The best way to prevent staph is to keep hands and wounds clean. Most staph skin infections are easily treated with antibiotics or by draining the infection. Some staph bacteria such as MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) are resistant to certain antibiotics, making infections harder to treat.
Viral Skin Infections
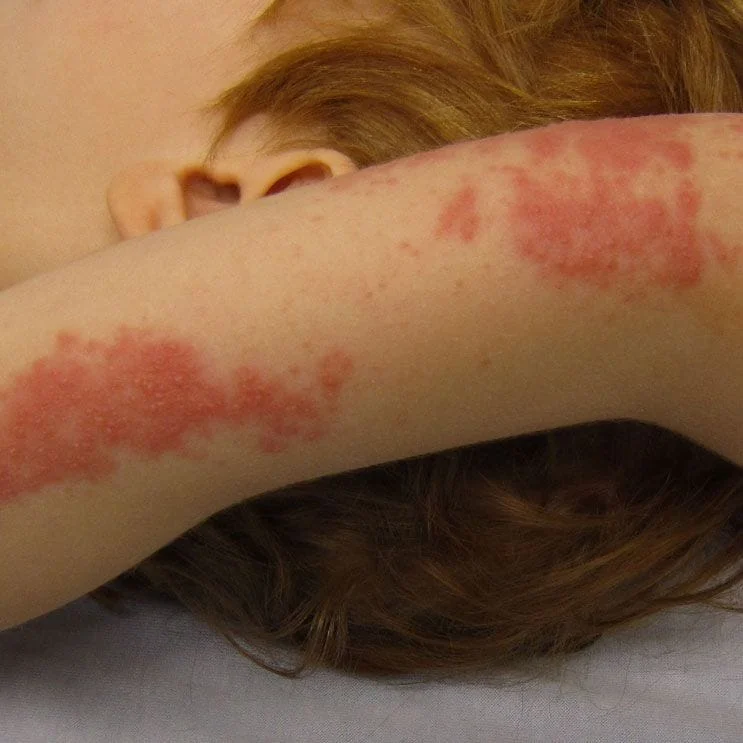
Shingles
Shingles is a disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus – the same virus that causes chickenpox. After you have chickenpox, the virus stays in your body. It may not cause problems for many years. As you get older, the virus may reappear as shingles. Although it is most common in people over age 50, anyone who has had chickenpox is at risk.
The virus spreads through direct contact with the rash, and cannot spread through the air. Early signs of shingles include burning or shooting pain and tingling or itching, usually on one side of the body or face. Rashes or blisters appear anywhere from one to 14 days later. There is no cure for shingles. Early treatment with medicines that fight the virus may help. These medicines may also help prevent lingering pain. A vaccine may prevent shingles or lessen its effects. The vaccine is recommended for people 60 or over. In some cases doctors may give it to people ages 50 to 59.:
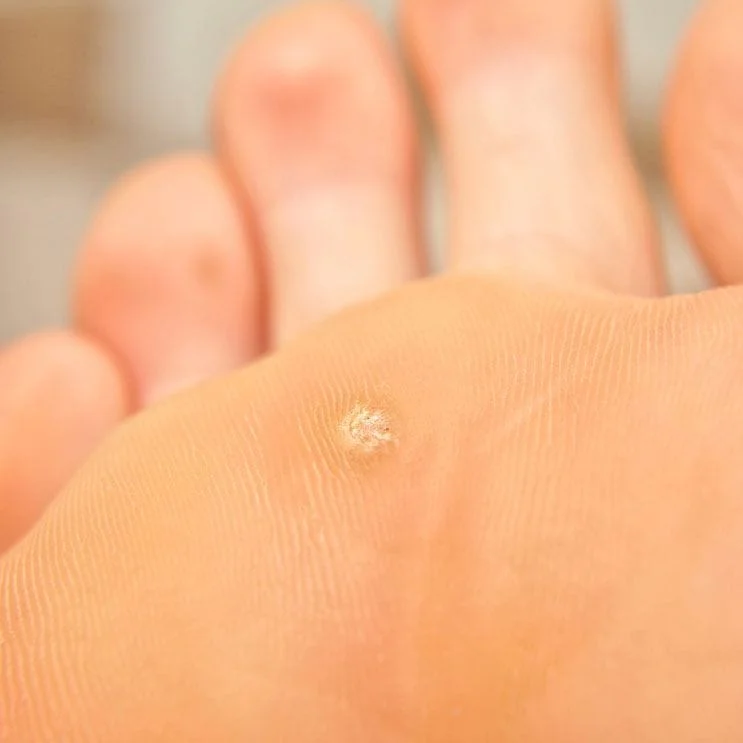
Warts
Warts are benign (not cancerous) skin growths that appear when a virus infects the top layer of the skin. Viruses that cause warts are called human papillomavirus (HPV). You are more likely to get one of these viruses if you cut or damage your skin in some way.
Types of warts include:
- Common warts, often on fingers
- Plantar warts, often on soles of your feet
- Genital warts, an STD
- Flat warts, often in places you shave
In children, warts often go away on their own. In adults, they tend to stay. If they hurt or bother you, or if they multiply, you can remove them. Chemical skin treatments usually work. If not, various freezing, surgical and laser treatments can remove warts.
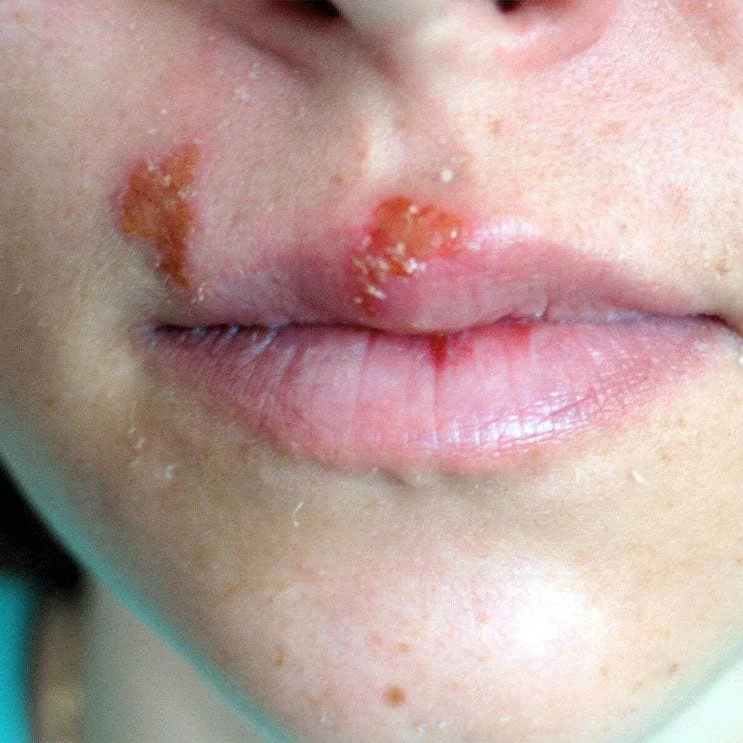
Herpes Simplex
Herpes is an infection that is caused by a herpes simplex virus (HSV). Oral herpes causes cold sores around the mouth or face. Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and affects the genitals, buttocks or anal area. Other herpes infections can affect the eyes, skin, or other parts of the body.
There are two main types of HSV:
- HSV type 1 – main cause of cold sores
- HSV type 2 – main cause of genital herpes
HSV spreads through direct contact. Some people have no symptoms. Others get sores near the area where the virus has entered the body. They turn into blisters, become itchy and painful, and then heal. Most people have outbreaks several times a year. Over time, you get them less often. Medicines to help your body fight the virus can help lessen symptoms and decrease outbreaks.
Viral Skin Infections
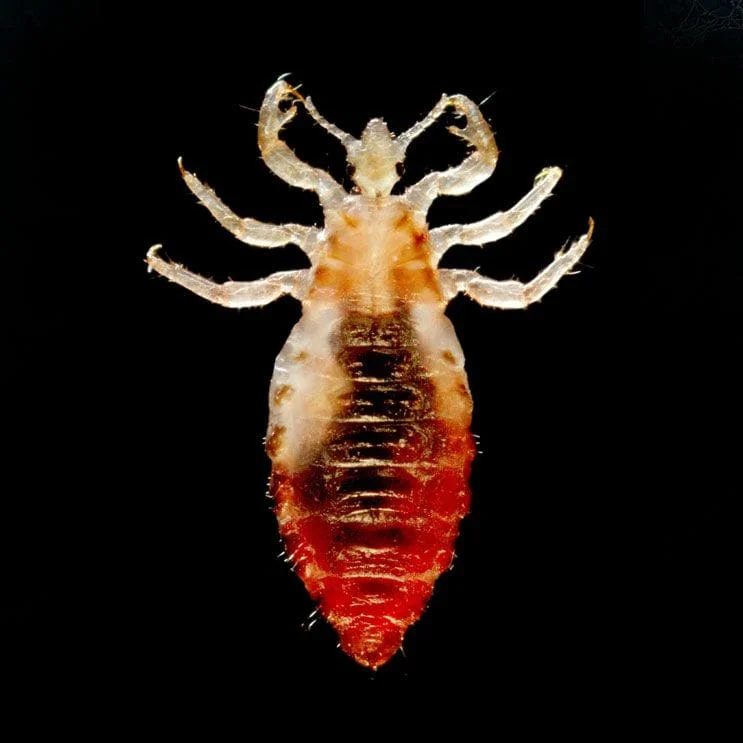

Body Lice
Lice are parasitic insects that can be found on people’s heads and bodies. They survive by feeding on human blood. Lice found on each area of the body are different from each other. The three types of lice that live on humans are head lice, body lice (also called clothes lice), and pubic lice (“crabs”).
Symptoms of lice may include:
- Intense itching
- Rash
- Visible nits (lice eggs) or crawling lice
Lice spread most commonly by close person-to-person contact. Dogs, cats, and other pets do not spread human lice. Lice move by crawling. They cannot hop or fly. If you get lice, both over-the-counter and prescription medicines are available for treatment.
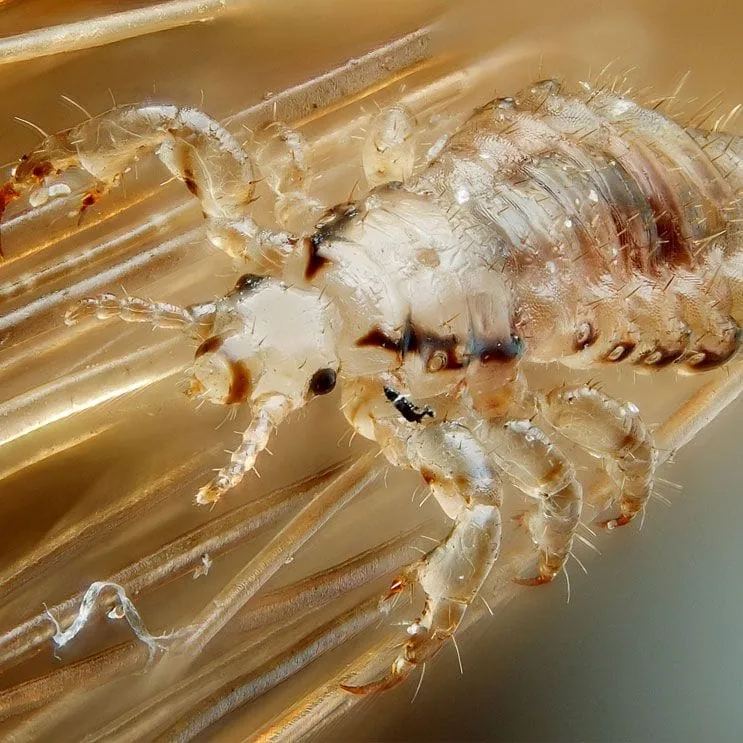

Head Lice
Head lice are parasitic wingless insects. They live on people’s heads and feed on their blood. An adult louse is about the size of a sesame seed. The eggs, called nits, are even smaller – about the size of a knot in thread. Lice and nits are easiest to detect at the neckline and behind the ears. Head lice are extremely contagious.
Symptoms include:
- Tickling feeling in the hair
- Frequent itching
- Sores from scratching
- Irritability and difficulty sleeping
Treatment for head lice is recommended for people with an active infestation. All household members and other close contacts should be checked. Anyone who has an active infestation should be treated. All infected people and their bedmates should be treated at the same time.
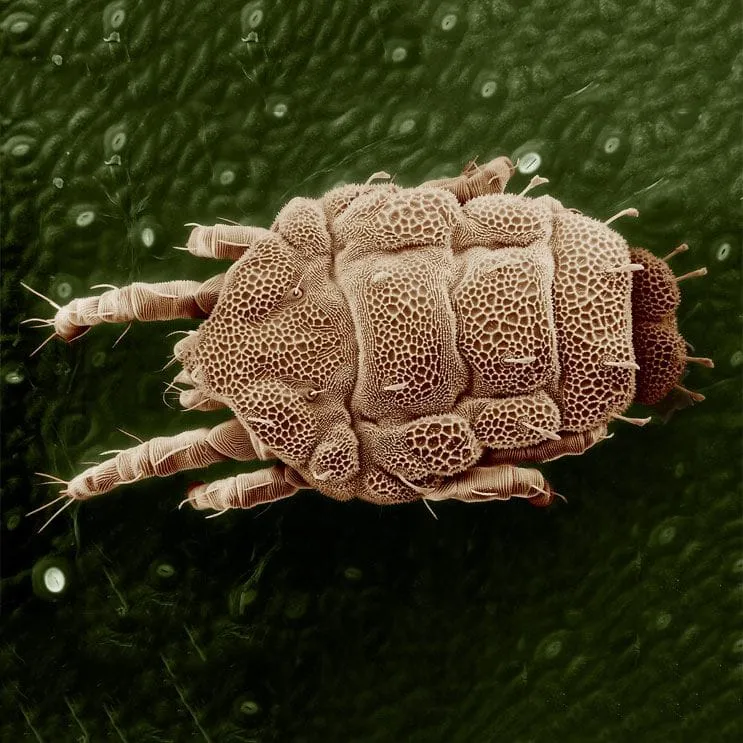

Scabies
Scabies is an itchy skin condition caused by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabei. It is common all over the world, and can affect anyone. Scabies spreads quickly in crowded conditions where there is frequent skin-to-skin contact between people.
Symptoms include:
- Pimple-like irritations or a rash
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Sores caused by scratching
Your health care provider diagnoses scabies by looking at the skin rash and finding burrows in the skin. Several lotions are available to treat scabies. The infected person’s clothes, bedding and towels should be washed in hot water and dried in a hot dryer. Treatment is also recommended for household members and sexual partners.

Athlete's Foot
Athlete’s foot is a common infection caused by a fungus. It most often affects the space between the toes. Symptoms include itching, burning, and cracked, scaly skin between your toes. You can get athlete’s foot from damp surfaces, such as showers, swimming pools, and locker room floors.
To prevent it
- Keep your feet clean, dry, and cool
- Wear clean socks
- Don’t walk barefoot in public areas
- Wear flip-flops in locker room showers
- Keep your toenails clean and clipped short
Treatments include over-the-counter antifungal creams for most cases and prescription medicines for more serious infections. These usually clear up the infection, but it can come back.

Yeast Infection
Candida is the scientific name for yeast. It is a fungus that lives almost everywhere, including in your body. Usually, your immune system keeps yeast under control. If you are sick or taking antibiotics, it can multiply and cause an infection.
Yeast infections affect different parts of the body in different ways:
- Thrush is a yeast infection that causes white patches in your mouth
- Candida esophagitis is thrush that spreads to your esophagus. It can make it hard or painful to swallow
- Women can get vaginal yeast infections, causing itchiness, pain and discharge
- Yeast infections of the skin cause itching and rashes
- Yeast infections in your bloodstream can be life-threatening
Anti-fungal medicines get rid of yeast infections in most people. If you have a weak immune system, treatment might be more difficult.
